The Internal Revenue Service is expanding its oversight of digital asset transactions, and Form 1099-DA represents one of the most significant regulatory developments affecting cryptocurrency investors, traders, and businesses. As digital assets become more integrated into the financial system, tax reporting expectations are shifting toward greater structure, transparency, and enforceability.
What Is Form 1099-DA
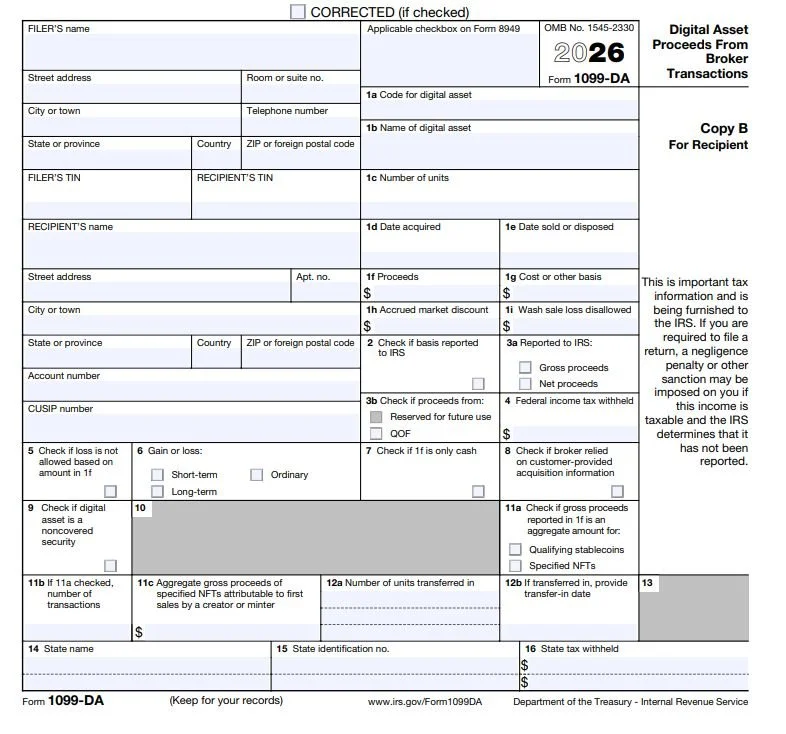
Form 1099-DA, Digital Asset Proceeds From Broker Transactions, is a new information return required under Internal Revenue Code Section 6045, as amended by the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. The form is designed to report proceeds from the sale or disposition of digital assets, including cryptocurrencies and certain stablecoins.
Under IRC Section 6045(g)(3), digital assets are treated similarly to specified securities for information reporting purposes, placing digital asset brokers under reporting obligations historically applied to stock and bond transactions.
Who Must Issue Form 1099-DA
IRC Section 6045(c)(1) defines a broker as any person who, for consideration, regularly acts as an intermediary with respect to sales of property. Recent amendments expanded this definition to include digital asset brokers who facilitate transfers or dispositions on behalf of customers.
As a result, centralized cryptocurrency exchanges and other qualifying intermediaries are generally required to issue Form 1099-DA to customers and file copies with the IRS. The application of these rules to decentralized platforms continues to evolve as Treasury regulations are finalized.
What Information Is Reported
Form 1099-DA reports gross proceeds from digital asset dispositions, consistent with IRC Section 6045(a). At this stage, cost basis reporting may be limited depending on the type of digital asset and the broker’s ability to track historical transaction data.
It is critical to note that gross proceeds alone do not determine taxable income. Under IRC Section 1001(a), taxable gain or loss is calculated as the difference between the amount realized and the taxpayer’s adjusted basis in the asset.
Why This Matters for Taxpayers
Even if a taxpayer receives Form 1099-DA, the responsibility for accurate reporting remains with the taxpayer. IRC Section 6001 requires taxpayers to maintain sufficient records to substantiate income, deductions, and basis.
Relying solely on Form 1099-DA without reconciling personal records can lead to overstated taxable income or underreported losses, particularly where cost basis is incomplete or missing.
Increased Enforcement and Transparency
Form 1099-DA reflects the IRS’s broader effort to increase compliance in the digital asset space. IRC Section 7602 grants the IRS broad authority to examine records and verify information returns, reinforcing the importance of accurate reporting.
Additionally, failure to properly report digital asset transactions may expose taxpayers to accuracy-related penalties under IRC Section 6662, as well as information return penalties under IRC Sections 6721 and 6722 when applicable.
Practical Steps to Prepare
Taxpayers engaging in digital asset transactions should strengthen their documentation practices by tracking acquisition dates, cost basis, transaction fees, wallet transfers, and taxable events.
Need Help With Form 1099-DA or Digital Asset Tax Reporting?
If you have questions about Form 1099-DA, cryptocurrency reporting, or how digital asset transactions impact your tax return, our team at JCox CPAs & Advisors, P.C. is here to help. We work with individuals and businesses to ensure digital asset activity is reported accurately, compliantly, and in line with current IRS guidance.
Whether you need help reconciling Forms 1099-DA, calculating gains and losses, or filing your tax return with confidence, reach out to JCox CPAs & Advisors, P.C. to get your questions answered and your taxes filed correctly.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the uncertainty out of digital asset tax reporting.